As the web has grown more complicated thanks to technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences, the need for specialized developers is also on the rise. Sure, it is great to have developers who are experts in basic frontend technologies. Then, there are some who know the best backend frameworks from the back of their hand.
However, the wave of expert full-stack developers who carry both frontend and backend tasks cannot go unnoticed. Multiple studies have shown that the demand for full-stack developers has gone up by 20% in the last few years.
This article discusses who full-stack developers are, what they do, and what they should focus on to succeed in this competitive environment. Let us begin:
Who is a full-stack developer?
Put merely: full-stack developers are engineers who work with both the frontend and backend of a website or an application and primarily tackle projects involving databases, servers and systems engineering, building user-facing websites for clients, or working with multiple businesses during the planning phase of projects.
Typically, efficient full-stack developers would be proficient in several programming languages and databases such as HTML, PHP, JavaScript, and CSS—although, over time, they build their specialty in one or two languages only.
What does a full-stack developer do?
You will agree that full-stack developers are informally known as the Swiss Army knife of the software development world. Imagine having the ability to deliver end-to-end full-stack web development services to a client. That has got to be a highly marketable and agile skillset, right? Exactly! It is.
Full-stack developers are typically involved in the following activities:
- Translate user needs to system requirements by facilitating the use of architectures and implementing new systems
- Create servers and databases for enhanced functionality
- Work with several programming languages and write backend codes in Ruby, Python, and PHP,APIs and frontend codes in HTML and JavaScript
- Validate and monitor the performance of applications and infrastructure against the client brief
- Ensure responsiveness of software applications
- Troubleshoot the software app by deploying a fast and accurate solution in real-time
- Understand, create and debug database-related queries
- See-through a project from conception to finished product and communicate with the client continuously
How much do full-stack developers earn?
According to Payscale.com, a full-stack developer with 1-4 years of experience earns around $74,819 per annum. A mid-career full-stack developer with 5-9 years of work-ex makes an annual compensation of $92,012.
What skills are full-stack developers required to acquire?
In the last two years, full-stack development has moved beyond the usual realm of coding. Today, professionals in this field have also started upskilling themselves in project management, web design, and visual language (UI/UX) to deliver a more wholesome offering.
Apart from that, it is not uncommon to see a full-stack developer acquiring the following skills:
- Expertise in one or more third-party libraries such as Angular and ReactJS
- Knowledge in “version control” to manipulate and create database queries
- Experience with databases and caching
- Understanding of security concerns and best user experience practices
- Soft skills such as time management, attention to detail, team management
Seven things all full-stack developers must know to be successful
A full-stack developer has a broad technical profile, understands both backend tasks and basic frontend technologies, and is increasingly in high demand in the marketplace. Therefore, here are seven things that all full-stack developers must know to beat the competition, raise the bar for themselves, and add more value to businesses:
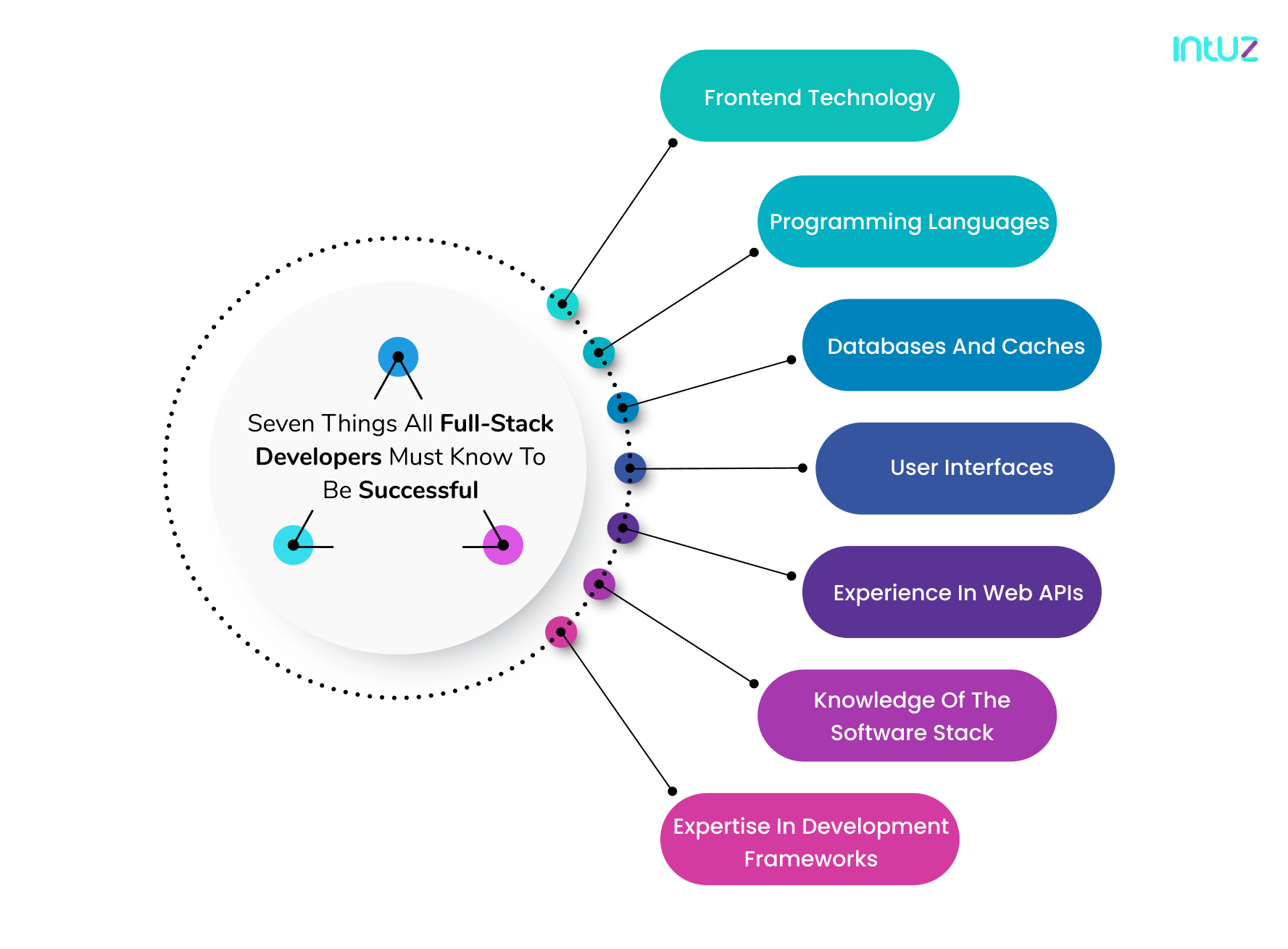
1. Frontend technology: the face of the website
Whatever the time and trend might be, any website must rank high on the following three elements:
- Complexity – the user interface of the website that impacts user engagement
- Usability – the attribute denotes the easy-to-use website aspect
- Compatibility – the ability to adapt to different web browsers
It is pretty evident from first glance that those full-stack developers that primarily deal with website development cannot ignore these three elements. Hence, they must have an idea about JavaScript—the most popular programming language for all developers.
JavaScript is the first language that defines the function of a web page. It is used for enhancing many audio and video features, protocols for scrolling or navigating the page, closures for page animation implementation, and others.
Full-stack developers should master basic frontend technologies such as CSS3, HTML5, and JavaScript. They should also have a good command over third-party libraries or frameworks like SASS, LESS, AngularJS, jQuery, ReactJS, and so on.
2. Programming languages: pillars of the website
Programming languages are a set of code that tells an application of how it is supposed to perform. They provide logic to the application to perform a task and get a predetermined output from the action. Let us study an example: when burning a CD, the user must paste something in the pen drive to transfer that data onto the CD.
The communication between hardware and software happens because of the programming languages. The same logic is applied in websites—without the software. A skilled full-stack developer should be proficient in programming languages such as Java, PHP, Ruby, C#, and Swift. (Do follow) This particular skill set is non-negotiable—if they want to make a mark in the industry.
For the full-stack developers to be successful, it is necessary to be a master in the language syntax and familiarize oneself with the concept of designing, structuring, testing, and implementing the website code efficiently. That is because of the higher demand for improved computation capabilities of modern software applications.
3. Understanding of databases and caches
Life without data is impossible. Business without information is impossible. Do not be surprised when we tell you we produce 2.5 quintillion bytes of data every day. Given the obscene number, it is essential to handle large amounts and multiple data types efficiently. No wonder the demand for database management systems (DBMS) and database caching is at an all-time high.
If the full-stack developers have experience working with various DBMS technologies such as SQLServer, Redis, Oracle, MySQL, MongoDB, then that is a plus. After all, every software application needs a database to store and organize data.
Full-stack development deals with databases and ensures they interact seamlessly. Developers use that knowledge to build the backend for dynamic applications. Moreover, the speed of the database impacts the overall application performance.
Slow processing queries, high costs to scale, and the need for simplifying data access—all of these issues can be handled or rectified if the developer knows how to do data caching and thus be more successful. On the other hand, designing and manipulating database queries and learning how to work with XML and JSON make the application more efficient.
4. Basics of designing user interfaces
The success of a business stems from how well they know their users—including understanding their goals, preferences, skills, and tendencies. Once those insights have been garnered, it is necessary to build an application where:
- The user interface is simple, without any unnecessary elements
- UI elements used are consistent yet add to the patterns in the layout and design
- The spatial relationships between the page’s structure and its items make sense
- Colors, typographies, and textures are appropriately used
A responsive app design helps the business establish its brand in the market. Therefore, to be successful as a full-stack developer, knowledge of design is paramount. It is necessary to be aware of the basic design techniques that add to creating user-friendly websites that appeal to the users.
Furthermore, knowledge about the fundamental design principles (UI/UX) and essential design utility (code, copy, SEO) are also welcomed.
5. In-depth experience in web APIs
The term “web API” refers to both sides of the computer system interacting with each other over a network, i.e., the API services offered by the client (e.g., a web browser) and the API services provided by a server.
The latter is a programmatic interface to a defined request-response message system. There are several design models for web APIs used by today’s developers, the most popular being SOAP and REST.
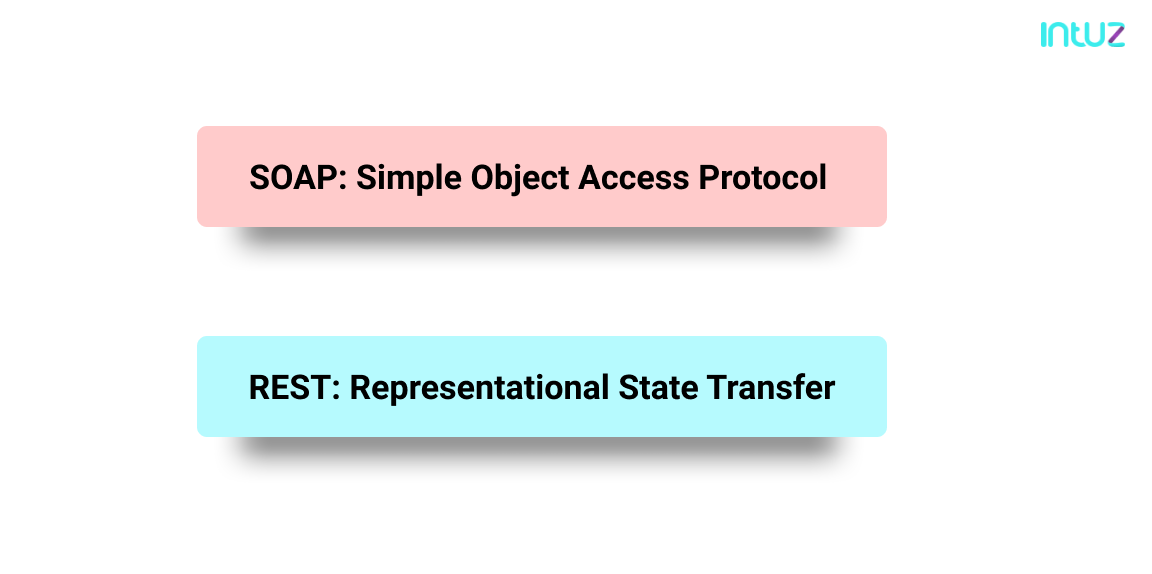
SOAP is the perfect choice for distributed enterprise environments and is language, platform, and transport dependent. A full-stack developer can provide significant pre-build extensibility and built-in error handling capabilities, along with automation—if used with certain programming language elements.
REST is easier to use for developers of all experiences and is more flexible thanks to its easy-to-understand standards such as OpenAPI Specification 3.0. With REST, a full-stack developer can assume direct point-to-point communication.
REST stands a it closer to other web technologies concerning the design philosophy. Another good thing is its learning curve is too low.
6. Knowledge of the software stack: MEAN, MERN, and LAMP
Technically speaking, the software stack consists of operating systems, languages, databases, tools, scripting languages, and frameworks used by a full-stack developer to ease the workflow and develop a complete software solution. Developers must know three main stacks, including:
a. MEAN

MEAN is an acronym for MongoDB, ExpressJS, AngularJS, and NodeJS. A popular tech stack, it enables the use of a single programming language throughout the stack. Full-stack developers can reuse the code across the application, thus decreasing their efforts to reinvent the wheel.
b. MERN

On the other hand, MERN is actually an updated version of MEAN and helps developers in the rapid and efficient full-stack development. It offers them a better understanding of server-side and client-side because of the core use of JavaScript for software development.
c. LAMP

LAMP is an acronym for Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP. Full-stack developers love it for its flexibility and reliability. It offers simplicity and stability coupled with power, making it a suitable source for full-stack development.
7. Expertise in development frameworks
Programming languages are accompanied by a robust development framework such as Python Django, Ruby, MyBatis, Node.JS, PHP ThinkPHP,torrent files, and so on. Therefore, full-stack developers need to understand the development frameworks and know how to apply them efficiently in the business logic.
Knowing the fundamentals of web architecture, data structure, code structure, and the location of computational tasks helps them develop software applications from scratch. Proper planning of the architecture eliminates unnecessary confusion and allows the full-stack developers to do their job correctly.
Wrapping it up
Full-stack developers are essential “jack of all trades” and oscillate between basic frontend technologies and backend frameworks. Their job is to look at every aspect of software development critically and with attention to detail. They work on all three layers of the development process, including the logic layer, presentation layer, and data layer.
Those who are willing to continually update their industry knowledge, learn new programming techniques, and stay on track with the latest development tools are bound to carve a niche for themselves in the world of full-stack development.
Follow Technoroll for informative articles






